藥品名稱
drug name | (自費) Priorix 0.5mL/vial (Measles, Mumps & Rubella Virus Vaccine), |
| 藥檔狀態 | 使用中 |
成 份
Ingredient | Measles,Mumps&Rubella Virus Vaccine |
| 單位含量 | 1 dose/ 0.5mL/ vial |
| Dosage Forms | Injection, powder for reconstitution [preservative free] : 0.5mL/vial |
| 外觀描述 | |
| Appearance | |
廠商名稱
Manufacturer | 荷商葛蘭素史克藥廠股份有限公司臺灣分公司 |
製 造 商
Manufacturer | FIDIA FARMACEUTICI S.P.A. |
字 號
Product ID | 衛署菌疫輸字第000510號 |
藥理分類
Pharmacologic Category | Vaccine; Vaccine, Live (Viral) |
作用機轉
Mechanism of action | As a live, attenuated vaccine, MMR vaccine offers active immunity to disease caused by the measles, mumps, and rubella viruses. |
| 用途/適應症 | |
| Use |
Measles, mumps, and rubella prevention: Active immunization for simultaneous vaccination against measles, mumps, and rubella in patients ≧12 months of age
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommends routine vaccination for the following (CDC/ACIP [McLean 2013]):
‧ All children (first dose given at 12 to 15 months of age)
‧ Adults born in 1957 or later (without evidence of immunity or documentation of vaccination). Vaccine may be given to adults born prior to 1957 if they do not have contraindications to the MMR vaccine.
‧ Adults at higher risk for exposure to and transmission of measles, mumps, and rubella should receive special consideration for vaccination, unless an acceptable evidence of immunity exists. This includes international travelers, persons attending colleges and other post high school education, persons working in health care facilities.
|
衛福部核准適用症狀
MOHW approved indications |
麻疹、腮腺炎及德國麻疹之主動免疫。
|
| 常用劑量 |
(藥品劑量會因人或病情增減,請依照醫師指示服用。) |
| Dose |
【Adult】
Note: The minimum interval between 2 doses of MMR vaccine is 28 days (CDC/ACIP [McLean 2013]).
Immunization: SubQ: 0.5 mL per dose; 1 or 2 doses administered at least 28 days apart based upon the following criteria (CDC/ACIP [McLean 2013]).
Adults born in or after 1957 should be vaccinated with ≧1 dose unless they have acceptable evidence of immunity.
Adults born prior to 1957 are considered immune to measles, mumps, and rubella but may be vaccinated with 1 or 2 doses if they do not have contraindications to the vaccine. Pregnant adults born prior to 1957 are not considered immune to rubella.
Adults who received inactivated or unknown type of measles vaccine during 1963 to 1967: One or two doses of MMR.
Adults who received inactivated or unknown type of mumps vaccine before 1979 and who are at high risk: Two doses of MMR.
Health care personnel: Persons born in or after 1957 should have 2 doses of vaccine unless they have acceptable evidence of immunity. Unvaccinated persons born prior to 1957 should also consider vaccination with 2 doses of MMR for measles and mumps or 1 dose of MMR for rubella unless they have laboratory evidence or laboratory confirmation of disease (CDC/ACIP [McLean 2013]).
HIV infection (without severe immunosuppression): Two doses of MMR unless there is acceptable evidence of immunity.
Household/close contacts of immunocompromised persons: Two doses of MMR unless there is acceptable evidence of immunity.
International travelers: Two doses of MMR prior to travel unless there is acceptable evidence of immunity.
Measles, mumps, or rubella outbreak (community): Adults who received 1 dose of MMR should be considered for a second dose if the outbreak involves measles or mumps in adults. Vaccination should also be considered for persons born prior to 1957 without evidence of immunity who may be exposed to mumps. A single dose of a rubella-containing vaccine is considered adequate vaccination during a rubella outbreak. During a mumps outbreak, a third dose of MMR vaccine is recommended for at-risk persons who have been previously vaccinated with 2 doses (CDC/ACIP [Marin 2018]; Cardemil 2017); consult local public health authorities.
Measles, mumps, or rubella outbreak (healthcare facility): Unvaccinated health care personnel without evidence of immunity regardless of birth year should receive 2 doses during a measles or mumps outbreak and one dose during a rubella outbreak.
Students: Persons entering post high school educational facilities should receive 2 doses of MMR unless they have acceptable evidence of immunity prior to enrollment.
Women of childbearing potential: One dose of MMR unless they have acceptable evidence of immunity. Vaccination should not be given during pregnancy and pregnancy should be avoided for 28 days after vaccine administration.
【Pediatric】
Note: The minimum interval between two doses of MMR vaccine is 28 days (CDC/ACIP [McLean 2013]). Refer to Additional Information for a description of acceptable evidence of immunity. Consult CDC/ACIP annual immunization schedules for additional information including specific detailed recommendations for catch-up scenarios and/or care of patients with high-risk conditions. According to ACIP, doses administered ≦4 days before minimum interval or age are considered valid; however, local or state mandates may supersede this timeframe (ACIP [Kroger 2021]).
Primary immunization: Children ≧12 months: SubQ: 0.5 mL per dose for a total of 2 doses given as follows: 12 to 15 months of age and the second dose at 4 to 6 years of age; the second dose is recommended prior to entering kindergarten or first grade. The second dose may be administered at any time provided at least 28 days have elapsed since the first dose (CDC/ACIP [McLean 2013]).
Catch-up immunization (CDC/ACIP [McLean 2013]): School-aged Children and Adolescents: Ensure that 2 doses have been given at least 28 days apart.
Measles outbreak without acceptable evidence of immunity and at risk for exposure: Note: Should be administered within 72 hours postexposure.
- Infants 6 to 11 months: SubQ: 0.5 mL per dose as a single dose (CDC/ACIP [McLean 2013]). Children should be vaccinated at ≧12 months with standard 2-dose series.
- Children 1 to 4 years: Children who received 1 dose (0.5 mL SubQ) of MMR should be considered for a second dose if the outbreak involves preschool-aged children (CDC/ACIP [McLean 2013]).
Mumps outbreak (eg, community):
- Children 1 to 4 years (without acceptable evidence of immunity and at risk for exposure): Children who received 1 dose of MMR should be considered for a second dose (0.5 mL SubQ) if the outbreak involves preschool-aged children (CDC/ACIP [McLean 2013]).
- Children and Adolescents (fully immunized [2 previous MMR doses]); community outbreak: A third dose of MMR vaccine may be considered; appropriate patients should be guided by public health officials (ACIP/CDC [Marin 2018]).
Household/close contacts of immunocompromised persons without acceptable evidence of immunity: Children ≧12 months and Adolescents: SubQ: 0.5 mL per dose for a total of 2 doses administered at least 28 days apart unless they have acceptable evidence of immunity (CDC/ACIP [McLean 2013]).
HIV infection without evidence of MMR immunity: Children ≧12 months and Adolescents: SubQ: 0.5 mL per dose. Children and adolescents with HIV infection and without evidence of severe immunosuppression should have 2 additional doses of MMR; those with perinatal HIV infection who were vaccinated prior to effective ART should have 2 additional doses of MMR once ART is established (CDC/ACIP [McLean 2013]).
International travel, without evidence of immunity (CDC/ACIP [McLean 2013]):
- Infants 6 to 11 months: SubQ: 0.5 mL per dose. Administer 1 dose of MMR before departure from the United States; these infants should be revaccinated with 2 doses of MMR with the first dose between 12 to 15 months of age (and at least 28 days after the previous dose; target 12 months of age if child remains in area where disease risk if high) and the second dose at least 28 days later.
- Children ≧12 months and Adolescents: SubQ: 0.5 mL per dose. Administer 2 doses of MMR before departure from the United States with the second dose at least 28 days later.
【Renal Impairment】
There are no dosage adjustments provided in manufacturer`s labeling.
【Hepatic Impairment】
There are no dosage adjustments provided in manufacturer`s labeling.
|
懷孕分級
Pregnancy Risk Factor |
依文獻內容判定系統稽核懷孕分級建置為:XM
UpToDate:
[Reproductive]
This vaccine should not be administered to women who plan to become pregnant within 1 month of immunization.
Prenatal screening is recommended for all pregnant women who lack evidence of rubella immunity. Women of childbearing age without documentation of rubella vaccination or serologic evidence of immunity should be vaccinated (for women of childbearing potential, birth prior to 1957 is not acceptable evidence of immunity to rubella).
Sterility in males and infertility in prepubescent females may occur with natural mumps infection (CDC/ACIP [McLean 2013]).
[Pregnancy]
Based on information collected following inadvertent administration during pregnancy, adverse events have not been observed following use of rubella vaccine. However, theoretical risks cannot be ruled out; use of this vaccine is contraindicated in pregnant females. The risk of congenital rubella syndrome following vaccination is significantly less than the risk associated following infection; therefore, inadvertent administration of MMR during pregnancy is not considered an indication to terminate pregnancy.
Adverse consequences of natural infection in unvaccinated pregnant women have been reported. Measles infection during pregnancy may increase the risk of premature labor, preterm delivery, spontaneous abortion and low birth weights. Rubella infection during the first trimester may lead to miscarriages, stillbirths, and congenital rubella syndrome (includes auditory, ophthalmic, cardiac and neurologic defects; intrauterine and postnatal growth retardation); fetal rubella infection can occur during any trimester of pregnancy. Maternal mumps infection during the first trimester may increase the risk of spontaneous abortion or intrauterine fetal death.
Prenatal screening is recommended for all pregnant women who lack evidence of rubella immunity. Women of childbearing age without documentation of rubella vaccination or serologic evidence of immunity should be vaccinated (for women of childbearing potential, birth prior to 1957 is not acceptable evidence of immunity to rubella). Women who are pregnant should be vaccinated upon completion or termination of pregnancy, prior to discharge. Household contacts of pregnant women may be vaccinated (CDC/ACIP [McLean 2013]).
仿單:禁用於懷孕婦女,接種疫苗後一個月內應避免懷孕。
-----------------------------------------------------------
[FDA(美國食品及藥物管理局)懷孕分級說明:
A:對照試驗無法證實懷孕初期及後期使用會危害胎兒。
B:動物試驗無法證實對胎兒有害,但缺乏人類對照試驗;或動物試驗有副作用報告,但無法證實對懷孕初期及後期之胎兒有害。
C:動物實驗中對胎兒有害但缺乏孕婦對照實驗;或無動物及孕婦試驗。
D:證實對胎兒有害,但疾病對孕婦有生命威脅或較安全藥品無法使用或無效時可使用。
X:證實對胎兒有害,且使用後危害大於可能的益處。孕婦及可能懷孕婦女禁用。]
|
| 禁忌症 |
1.不可用於對Neomycin或本疫苗的其他成分產生全身性過敏症狀患者(對雞蛋過敏者);對Neomycin有接觸性皮膚炎病史者,非本產品禁忌症。
2.禁用於過去施打麻疹、腮腺炎和(或)德國麻疹後曾出現嚴重過敏徵狀者。
3.禁用於有嚴重體液或細胞(原發或後天)免疫不全患者,如人類免疫缺損病毒感染徵候群。
4.禁用於懷孕婦女。接種疫苗後一個月內應避免懷孕。
|
| Contraindications |
Hypersensitivity to measles, mumps, and/or rubella vaccine or any component of the formulation (including gelatin and neomycin); active febrile illness (fever >38.5°C [>101.3°F]); active untreated tuberculosis; immunosuppressed or immunodeficient individuals due to disease or medical therapy; pregnancy.
|
| 常見副作用 | |
| Common adverse drug reactions | |
| Adverse Reactions |
Frequency not defined:
- Cardiovascular: Syncope, vasculitis
- Central nervous system: Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, ataxia, dizziness, Guillain-Barre syndrome, headache, irritability, malaise, paresthesia, polyneuropathy, retrobulbar neuritis, seizure, sensorineural hearing loss, subacute sclerosing panencephalitis, transverse myelitis
- Dermatologic: Erythema multiforme, IgA vasculitis (Henoch-Schnolein purpura/acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy), morbilliform rash, pruritus, rash, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, urticaria
- Endocrine & metabolic: Diabetes mellitus
- Gastrointestinal: Diarrhea, nausea, pancreatitis, parotitis, sore throat, vomiting
- Genitourinary: Epididymitis, orchitis
- Hematologic & oncologic: Leukocytosis, lymphadenopathy (regional), purpura, thrombocytopenia
- Hypersensitivity: Anaphylactoid reaction, anaphylaxis, angioedema
- Infection: Atypical measles
- Local: Injection site reaction (including burning, induration, redness, stinging, swelling, tenderness, vesiculation, wheal and flare)
- Neuromuscular & skeletal: Arthropathy (arthralgia/arthritis: Women 12% to 26%; children ≦3%), myalgia, panniculitis
- Ophthalmic: Conjunctivitis, oculomotor nerve paralysis, optic neuritis, optic papillitis, retinitis
- Otic: Otitis media
- Respiratory: Bronchospasm, cough, pneumonia, rhinitis
- Miscellaneous: Febrile seizures, fever
<1%, postmarketing, and/or case reports: Aseptic meningitis (associated with Urabe strain of mumps vaccine), brain disease, encephalitis
|
★高警訊藥品
監測建議 |
|
監測
Monitoring |
Monitor for anaphylaxis and syncope for 15 minutes following administration (ACIP [Kroger 2021]). If seizure-like activity associated with syncope occurs, maintain patient in supine or Trendelenburg position to reestablish adequate cerebral perfusion.
|
| 警語與注意事項 | |
| Warnings & precautions | |
| 針劑溶解條件 |
以所附稀釋液 (注射用水)溶解。(1100517 仿單資料)
|
| 針劑稀釋條件 |
|
| 針劑不相容性 |
不可與其他的疫苗在同一支注射針筒中混合。 (1100517 仿單資料)
|
| 針劑施打條件 |
不應採用血管內注射,以皮下注射方式投予。(1100517 仿單資料)
|
| 針劑保存安定性 |
‧ 稀釋前疫苗應貯存於溫度2-8℃間,稀釋液可貯存在冰箱或室溫中。
‧ 泡製後之疫苗必須立即使用。如果不能立即使用,已泡製的疫苗應貯存於2-8℃間,並且於泡製完成後8小時內使用完畢。(1100517 仿單資料)
|
最近修改日期時間
Updated | 6/23/2021 4:59:26 PM |
|
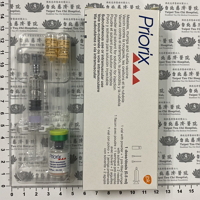
現用藥品
Available
|
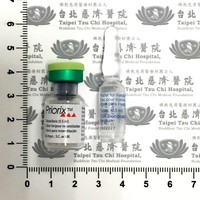
停用藥品
Old item
|

藥品仿單
DrugLabeling
|
|

二維條碼
QR code
|
|